The Windows registry stores critical system and application settings, and corruption can cause instability or crashes. Regular backups protect against failures and allow recovery using tools like Regedit, Command Prompt, or System Restore. Administrators can also restore via Safe Mode, Automatic Repair, DISM, or system reset if needed. Consistent registry backup practices and monitoring changes ensure reliable recovery and minimize downtime after system errors or malware damage.
The Windows registry is a database that contains important, machine-specific settings and information regarding almost everything in your computer — preferences, applications, users, attached devices and so on. The registry contains two basic elements: keys and values. The Windows operating system is constantly referring to the registry; for example, to open a program, install new software or change your hardware, Windows must check the values of certain keys.
A registry file can become corrupted due to malware or issues, which can lead to poor performance or even the operating system crashing. To ensure you can recover from corruption, you should back up your reg files regularly. So let’s find out how to make an entire registry backup and restore the registry in Windows.
Making a Windows Registry Backup
Back up the Windows Registry Using Regedit
Back up your registry regularly, and also before you attempt to change, create or remove registry settings or hives, or install new system drivers, so you can revert to a known good version if something goes wrong. Follow these steps to create a backup:
- Press the Windows button and the R button simultaneously to open the Run window.
- Type “regedit” to open the registry editor and press Enter.
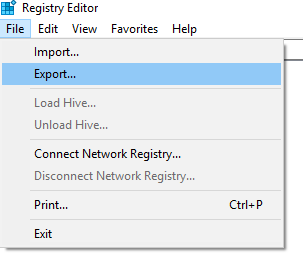
- Click File > Export.
- In the dialogue box, enter a name for the backup file (for example “rgbkp2018”), select the location where you want to export registry file and click Save to create and save the backup.
Backing up the Windows Registry Using the Command Prompt
You can export registry records by typing reg export and a particular registry root key at the command prompt. To export multiple keys, you can use a script like the following:
reg export HKCR C:RegBackHKCR.Reg /y reg export HKCU C:RegBackHKCU.Reg /y reg export HKLM C:RegBackHKLM.Reg /y reg export HKU C:RegBackHKU.Reg /y reg export HKCC C:RegBackHKCC.Reg /y
You can also back up your registry automatically with third-party registry cleaning software like CCleaner Registry Cleaner; you can find more about top free tools in the article “How to Perform Windows Registry Repair.”
Restoring the Windows Registry
You can restore your registry in several different ways. Here are the most common methods:
- From Safe Mode
- From the command prompt
- Using System Restore
- Using Automatic Repair
- Using System File Checker
- By resetting the PC
- Using the DISM command
- By reinstalling Windows from scratch
How to Restore a Registry Backup from Safe Mode
This is the most basic method. First, boot Windows in Safe Mode by pressing the F8 button while turning your computer on. When you boot in Safe Mode, Windows loads a minimal environment that helps ensure a stable system and protect vital files and drivers from corruption. Once you’ve booted into Safe Mode, perform the following commands:
- Press the Windows button and the R button simultaneously to open the Run window.
- Type “regedit” and press Enter.
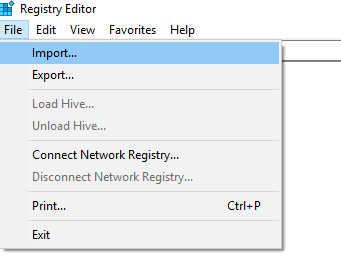
- Click File > Import to import a registry file.
- In the Import Registry dialogue box, browse to the location where you saved the file of your backup and click Open.
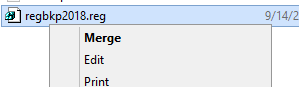
Alternatively, a slightly quicker method is to browse to the location with the backup, right-click the file and select Merge. The file will be automatically imported to your registry.
How to Restore the Registry from the Command Prompt
In some situations, the Windows system will not boot into Safe Mode, so you need to manually restore your registry from the command prompt. To do this, you’ll need your original Windows OS disk or an ISO image on the bootable flash drive with your Windows operating system.
Tap the F8 button before Windows starts and choose Repair My Computer. If F8 doesn’t work, boot from your CD or flash drive by selecting your CD-ROM or flash drive as a primary bootable device in the BIOS and enter the repair Windows mode from there. After booting the Windows OS setup, go to System Recovery and select the command prompt.
We’ll be assuming your Windows directory is located on the C drive. Enter these commands to change your working directory to the directory with your backup:
Cd /d C:windowsSystem32config xcopy *.* C:RegBack cd RegBack dir
Then replace the current registry settings with the ones from the backup using these commands:
copy /y software .. copy /y system .. copy /y sam ..
Note that the two periods are part of the command.
After this process completes, restart your computer.
How to Restore the Windows Registry with System Restore
You can also restore your computer’s registry using a Windows system restore point. If your computer has System Restore enabled, restore points will be created automatically when major changes are made to the system, such as the installation of new drivers. You can also create restore points manually.
- To open the System Restore window, click the Start menu and enter “restore” in the search box.
- Select System Restore from the list of results.
- Select a restore point. Windows will select the most recent restore point. If the registry corruption has been around for a while, click Show more restore points to see earlier ones. Each restore point will have a timestamp as well as a brief description of why the restore point was created.
- Click Scan for affected programs to see all of the programs and drivers that will be deleted from the computer and all programs that will likely not work correctly if you proceed with the restore. A system restore will not affect any of your personal files.
- Click Next and then Finish to start the restore process. This may take a few minutes. Your computer will reboot after the restore is complete.
How to Restore the Registry with Automatic Repair
Newer versions of Microsoft Windows, starting from Windows XP, include an automatic repair feature. When you run Automatic Repair, it will attempt to fix corrupt registry keys and repair invalid keys. In Windows 10, take these steps (note that in Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7, the steps might be different):
- Open the Settings
- Go to the Update & Security section and click
- On the Advanced Startup panel, click Restart now.
- After the computer reboots, on the Choose an option screen, click Troubleshoot.
- On the Advanced Options screen, click Automated Repair.
- Choose an account and log in when prompted to do so.
- Automatic repair will start. Your computer might reboot during this process.
How to Restore the Registry with System File Checker
Another way to fix a corrupted registry is to run the System File Checker:
- Run cmd.exe with administrator rights.
- In the command window, type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter.
- Wait until the scan is complete and then reboot if needed.
How to Restore the Registry by Resetting the PC
Windows 10 allows you to reset your computer and leave all your files untouched. This option completely refreshes your system files and may help with restoring the registry after a system crash. Here are the steps to follow:
- Go to Settings and click Update and Security.
- Select
- In the Reset This PC section, click Get Started and then click Keep My Files.
- Click Next twice and then click Finish.
Perform a Registry Restore with the DISM Command
- Run cmd.exe with administrator rights.
- Run the following command: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
- Wait until the scan process completes.
Reinstalling Windows from Scratch
If these methods didn’t fix your registry problems, then you probably will have to reinstall Windows from scratch, which will reset the registry to factory settings.
Conclusion
You should back up your registry on a regular schedule and before any major change so you can restore it if the installation of a program, driver or device causes issues. It is also important to track changes to your registry entries to quickly spot registry corruption. In particular, malware often changes registry startup keys so it will start automatically after each reboot. You can learn more about tracking Windows Server registry changes in this guide about detecting modifications to startup items in the Windows registry.
FAQ
How do you backup Windows registry before installing software?
Always backup your registry before making system changes or installing new software – it’s your safety net when things go wrong. The fastest method is using Registry Editor: press Windows + R, type “regedit,” then go to File > Export. Choose “All” to backup the entire registry, select a safe location like your Documents folder, and give it a descriptive name with the date.
For enterprise environments, PowerShell offers more control. Use these commands:
# Backup entire Local Machine hive
reg export HKLM backup-filename.reg
# Export specific software key
reg export "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\YourSoftware" backup-specific.regThe key is consistency – establish a naming convention and storage location that your team understands.
Remember that registry backups are snapshots in time. They capture your system’s current state, including all installed software, user settings, and system configurations. A backup taken before installing problematic software gives you a clean restoration point, but it won’t include any legitimate changes made after the backup. Plan accordingly and backup regularly, not just before major changes.
What should you do when registry backup fails?
Registry backup failures usually stem from permissions issues, corrupted registry sections, or insufficient disk space. First, run Registry Editor as administrator – right-click the Start button, select “Windows Terminal (Admin)” or “Command Prompt (Admin),” then type “regedit.” Administrative privileges are essential for accessing all registry sections.
If the backup still fails, try exporting specific registry hives instead of the entire registry. Start with HKEY_CURRENT_USER and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE separately. Large registries can timeout during export, so breaking them into smaller pieces increases success rates. Check your target drive for available space – registry backups can be several hundred megabytes.
For persistent failures, use the Windows built-in System File Checker:
sfc /scannowIf SFC finds issues, follow up with:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealthOnce the system is clean, registry backup should work normally. Don’t ignore backup failures – they often indicate underlying system problems that need attention.
How do you restore registry when Windows won’t boot?
When Windows won’t boot due to registry problems, you need to access recovery options before the operating system fully loads. Restart your computer and press F8 during startup to access the Advanced Boot Options menu. Select “Safe Mode” first – many registry problems don’t prevent Safe Mode from loading, and you can restore from there using Registry Editor.
If Safe Mode doesn’t work, use the Windows Recovery Environment. On Windows 10 and 11, interrupt the boot process three times to automatically trigger recovery mode, or boot from a Windows installation media and select “Repair your computer.” From the recovery environment, open Command Prompt and navigate to your registry backup location.
Use the reg import command to restore your backup:
reg import C:\path\to\your\backup.regIf you don’t have a recent backup, System Restore might help:
rstrui.exeThis launches System Restore where you can choose a restore point from before the problem started. Remember that System Restore affects registry settings, installed programs, and system files, but preserves personal data.
What’s the best location to store registry backup files?
Store registry backups in multiple locations to protect against drive failures and malware attacks. Your primary backup should go to a dedicated folder on your system drive – create “C:\RegistryBackups” for easy access during recovery scenarios. This location is accessible from Safe Mode and recovery environments when other drives might not be available.
Secondary backups belong on external media or network drives that aren’t constantly connected to your system. USB drives, external hard drives, or cloud storage provide protection against local system failures and malware. Many malware variants encrypt network drives, so avoid mapped drives for critical backups unless they’re properly air-gapped.
For enterprise environments, integrate registry backups into your existing backup infrastructure. Store them alongside system images and configuration backups, with proper retention policies and versioning. Document the backup locations in your disaster recovery procedures – registry backups are useless if your team can’t find them during an emergency. Consider automated backup scripts that rotate old files and maintain multiple versions.
How often should you backup Windows registry?
Registry backup frequency depends on how often you make system changes and your tolerance for data loss. For typical business workstations, weekly automated backups provide good protection without overwhelming storage. Systems that rarely change can backup monthly, while development machines or frequently updated servers need daily backups.
The key is backing up before significant changes. Always backup before installing new software, applying Windows updates, making group policy changes, or modifying system settings. These activities have the highest risk of registry corruption or unintended consequences. Automated scripts can handle routine backups, but manual backups before major changes give you precise restoration points.
Consider your recovery time objectives too. Recent backups mean faster recovery and less lost work, but they also consume more storage space. A good compromise is keeping daily backups for the past week, weekly backups for the past month, and monthly backups for the past year. This approach provides granular recent options while maintaining long-term recovery points for tracking down when problems first appeared.



