Zero Trust is not a fad but a proven security strategy built on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It strengthens defenses by enforcing least privilege, monitoring activity, and requiring continuous authentication. Organizations adopt ZT to combat credential theft, privileged account abuse, ransomware, and compliance challenges. With modern remote and hybrid workforces, Zero Trust reduces breaches, lowers costs, and enhances resilience against today’s evolving cyber threats.
It’s not your imagination; Zero Trust (ZT) is everywhere these days. Indeed, one study reports that 96% of security decision-makers say ZT is critical to their organization’s success, and another study notes that 51% of business leaders are speeding up their deployment of ZT capabilities.
But exactly what is Zero Trust and why is it the top security priority for organizations around the globe? More importantly, it is just a fad, or a valuable strategy that your organization needs to start adopting promptly? This article answers these questions, and also debunks common myths about Zero Trust.

What Zero Trust Is — and Is Not
Zero Trust is a security strategy that replaces the conventional wisdom of “trust, but verify” with a more stringent approach: “never trust, always verify.” In other words, a Zero Trust strategy involves treating every user, device, application and workload as untrustworthy and denying it access to any resources until it has been checked and authenticated.
Let’s debunk some of the biggest misconceptions about ZT:
- Myth: Zero Trust is new. Actually, the concept of ZT dates back to 2010 and many organizations have been guided by it for years.
- Myth: ZT is a tool or procedure. Zero Trust is a security strategy that typically requires multiple products, security controls, processes and procedures.
- Myth: Organizations can achieve full Zero Trust. Implementing Zero Trust, like any security strategy, is not a destination but a journey. You will need to keep adapting as your IT environment, the threat landscape, technology, tools, best practices and other factors evolve.
Top Drivers to Zero Trust Adoption
Why is Zero Trust a top security priority now? The single most important factor is the digital transformation that was needed to enable remote work during the Covid-19 pandemic. Rapid adoption of new technologies created new vulnerabilities that adversaries quickly began using to breach IT systems, launch devastating ransomware attacks and more. Faced with the increased risk of a data breach — which now cost an average of $4.24 million —organizations naturally began looking for ways to improve cybersecurity.
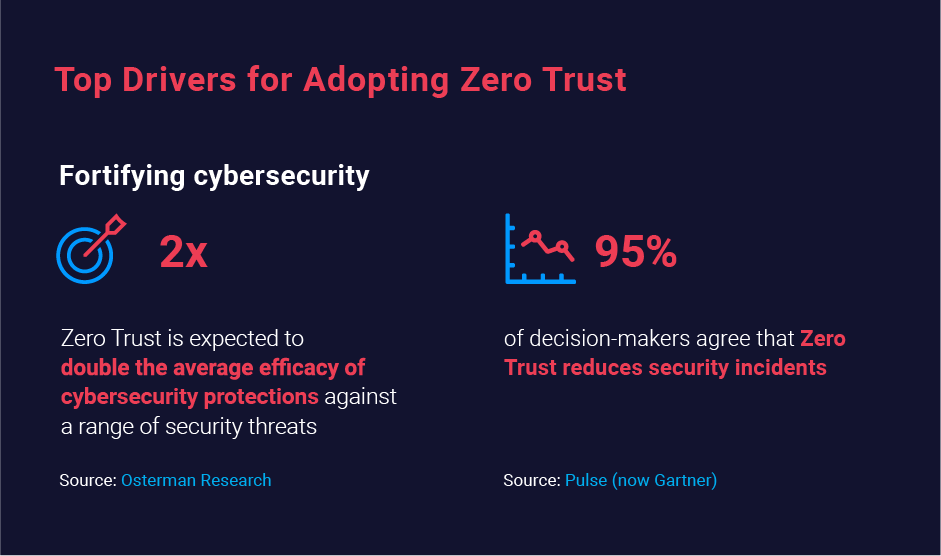
Zero Trust is an excellent option. In fact, Osterman Research reports that the average efficacy of cybersecurity defenses against a variety of threats is expected to double with a ZT architecture. Moreover, Zero Trust increases efficacy against data breaches in particular by 144 percent, from just 25 percent efficacy before ZT to 60 percent with a Zero Trust strategy in place.
Other research breaks down the top drivers for ZT adoption as follows:
51% — Modernizing cybersecurity program
43% — Reducing the number of security incidents
41% — Enabling secure remote access for employees and/or third parties
How Zero Trust Improves Cybersecurity
Exactly how does Zero Trust deliver these benefits? Here are the key ways that a ZT approach can enhance data security:
Protection against privileged account abuse
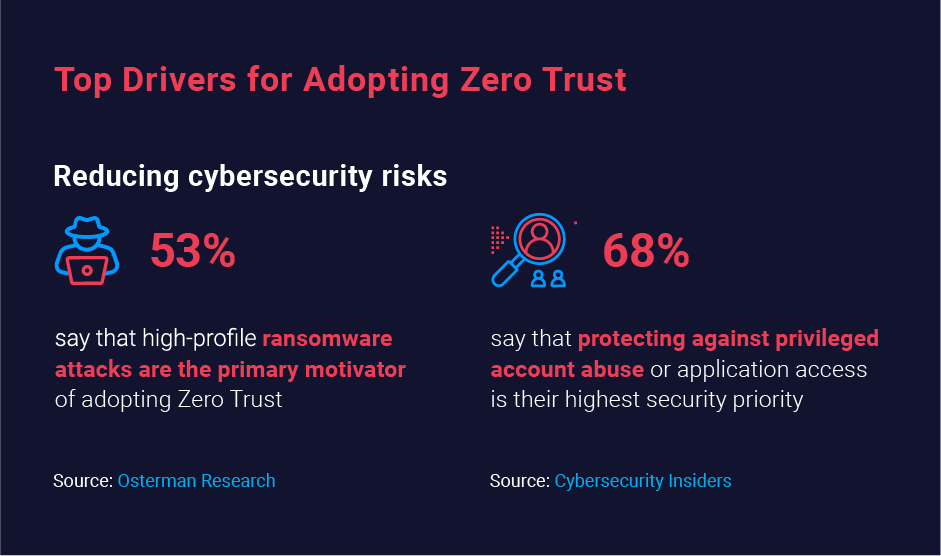
Attackers often target accounts that have elevated privileges, especially accounts with access to sensitive data and other resources. By embracing Zero Trust, organizations can reduce the risk from privileged accounts by:
- Strictly enforcing the least privilege principle to minimize the number of privileged accounts and the reach of each account
- Closely monitoring the activity of privileged accounts and changes to privileged groups, which enables security teams to quickly detect and respond to privilege escalation and suspicious use of privilege.
Protection against credential theft
Today, 20% of breaches are caused by compromised credentials, and the average cost for remediating credential theft incidents is $804,997, which makes credential theft the costliest security incident.
Adopting a ZT model can reduce the risks associated with credential theft. Strong account management practices will help prevent accounts from being compromised in the first place, and proper activity monitoring will help prevent accounts that are compromised from accessing sensitive resources. For example, with ZT, vital resources are protected with stronger controls, so an account attempting to read or copy sensitive data may be required to complete multifactor authentication, especially if the request is unusual for that account.
Protection against ransomware attacks
Osterman Research reports that 53% of respondents say ransomware attacks are their primary motivator for adopting a ZT model. Although ZT isn’t a panacea for ransomware, it can dramatically reduce an organization’s risk in multiple ways:
- Zero Trust involves adhering to the least-privilege principle and carefully controlling access to critical IT assess. Since ransomware relies on the privileges of the user account it has compromised, ZT limits the damage that a ransomware infection can do.
- A ZT strategy includes close monitoring of changes in the IT environment, which will facilitate quick detection of ransomware files being placed on a user’s machine, enabling IT teams to remove them before they can execute.
- ZT requires monitoring of activity in the IT environment and making reasoned decisions about whether to allow access, deny access or require additional verification. Therefore, it can help organizations respond to ransomware activity in time to minimize data exfiltration and other damage.
Protection of sensitive and regulated data
According to Osterman Research, the most common benefit of ZT is the ability to meet compliance requirements. A ZT approach recommends fine-grained separation of regulated data through micro-segmentation, along with strong identity and access management. As a result, ZT can help organizations demonstrate compliance with privacy standards and regulations like HIPAA, PCI DSS and GDPR, and have fewer findings during audits.

Summary
The modern reality of a remote or hybrid workforce and escalating cybercrime requires a modern approach to cybersecurity. Zero Trust has become the preferred approach for good reason: Implementing Zero Trust results in 50% fewer breaches and 40% less technology spending.
While implementing Zero Trust can seem like a daunting prospect, getting started is easy. By implementing core security best practices like least privilege and foundational tools like data classification and IT auditing, you can embark on your Zero Trust journey and start strengthening your cybersecurity right away.



